Comparison Between Forest Soil China With Tropical Peat Soil Sarawak
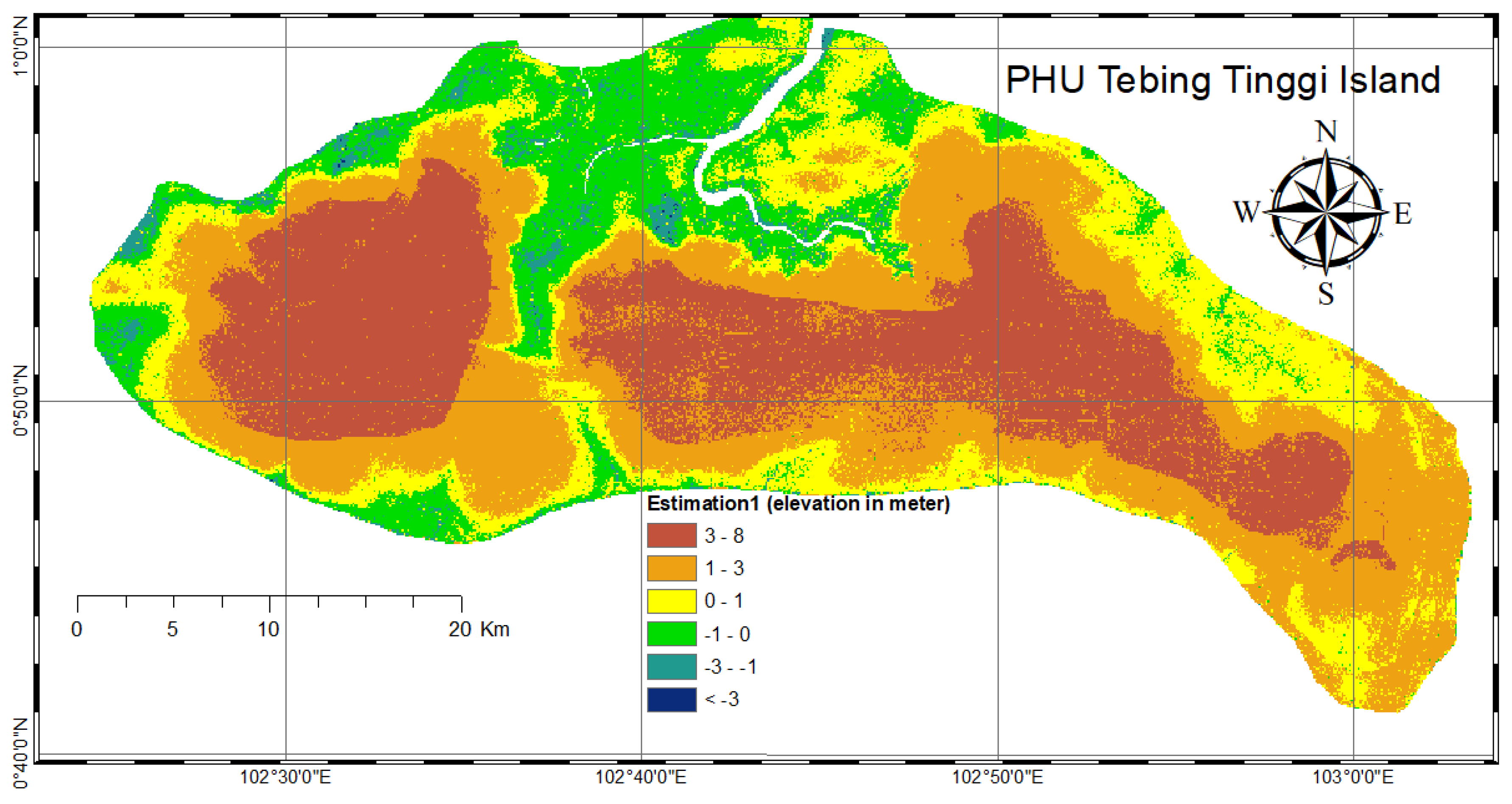
The terrain is relatively flat and homogenous across the site.
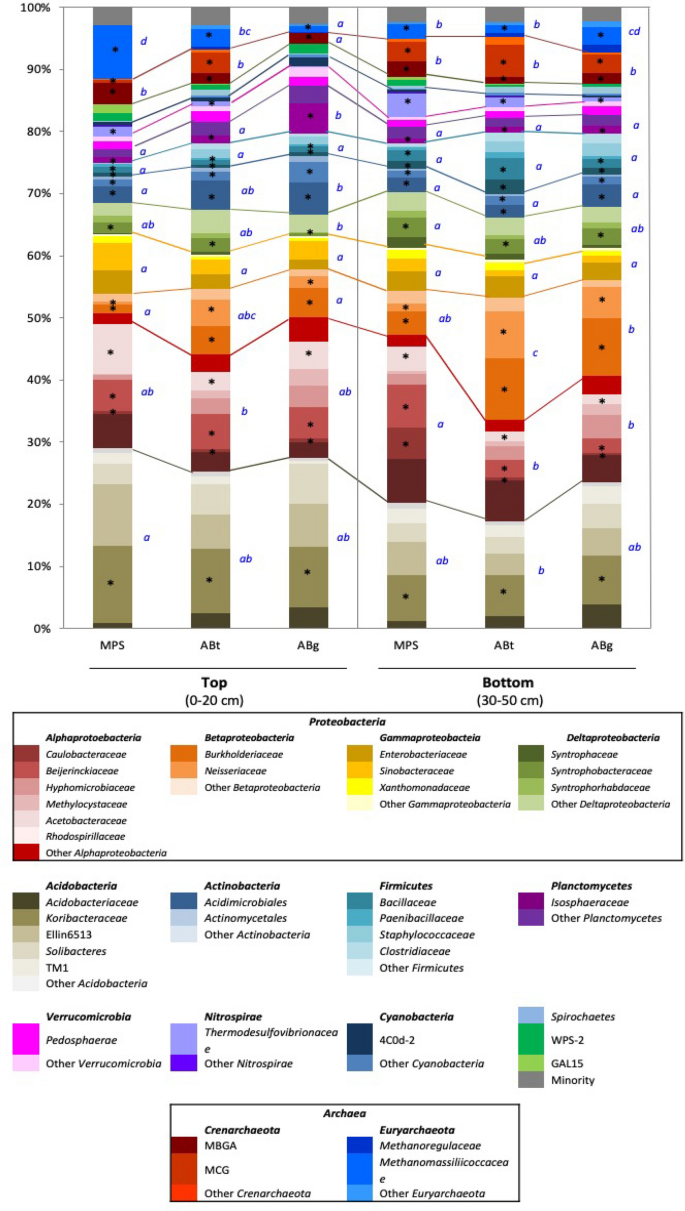
Comparison between forest soil china with tropical peat soil sarawak. Different physical properties such as organic content OC liquid limit LL fibre content FC specific gravity G s and engineering properties mainly the standard Proctor test have been conducted on remoulded peat soil samples. Soil microbial and root respirations from three ecosystems in tropical pea tland of sarawak mala ysia the soil could assist in the diffusion of oxygen-rich air and water soluble organic substrate. - 2008 East Malaysia Planters Association EMPA Conference 13-14 March Sandakan Sabah.
Ishikura and others 2018 especially in natural forests Itoh and others 2017. The main objectives of this review paper are to summarize and compare the geochemical properties of peat soil in different districts of Sarawak. Geochemical Properties of Peat Soil in Sarawak - A Review Teong Ing Tong1 a and Felix Ngee Leh Ling1 b 1Faculty of Civil and Env.
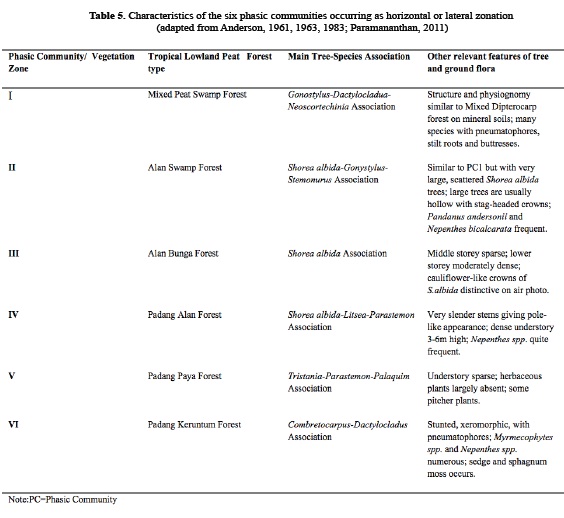
In comparison the AGB in logged-over peat swamp forest ranged between 65-167 t. Tropical peat mostly consists of dead organic matter from trees instead of spaghnum which are commonly found in temperate peat. Dominant vegetation in the overstory includes Shorea albida Gonystylus bancanus and Stemonurus spp.
The soil samples were analyzed for selected soil chemical. Also studies on soil CH 4 emissions are limited in tropical peatland. Several published figures suggest a much broader range of 73-323 t Cha.
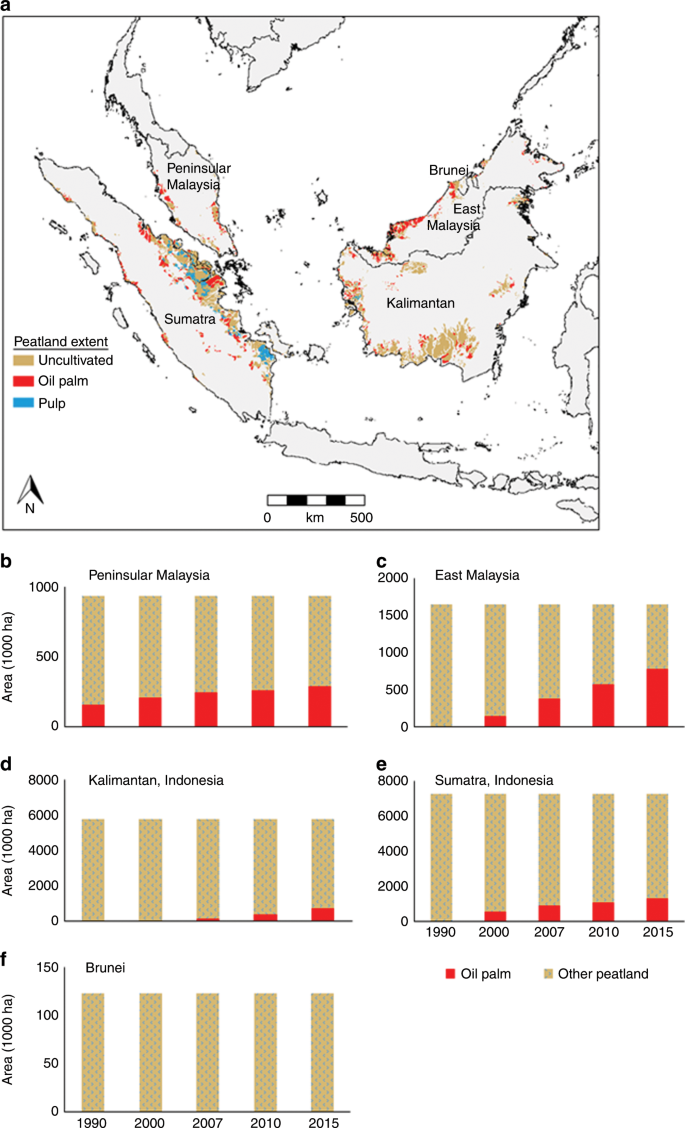
Tropical peat is a type of histosol that found in tropical latitude including South East Asia Africa and Central and South America. The Soil Division of Sarawak Malaysia has adopted a definition for organic soil that is based on profile partition ie. Owing to the huge soil carbon stock and high groundwater level GWL tropical peatlands potentially represent a significant source of methane CH 4to the.
Peat soil samples were taken at 0-15 cm depth in 6 plots with 01 ha each plot at Batang Igan forest at Sibu Sarawak Malaysia. Represents C loss from the peat soil. Geochemical properties Peat soil Organic matter Organic soil Engineering properties Abstract In geotechnical field peat soil is defined as soil.
Different physical properties such as organic content OC liquid limit LL fibre content FC specific gravity Gs and engineering properties mainly the standard Proctor test have been conducted on remoulded peat soil samples. Wakhid and others 2017. Comparison between paired means of soil carbon storage under the two different rainfall gradients were tested using paired t-test and correlation analysis was used to correlate variables pH soil organic matter total.
Soils that have 50 cm or more organic soil matter within 100 cm or more. This soil usually contain high organic matter content exceeding 75 with dry low bulk density around 02 mgm 3 00 grcu ft. High biomass productivity in conjunction with reduced carbon dioxide CO 2 emission from soil under the anoxic condition induced by high groundwater level GWL had made this ecosystem an efficient carbon C.
We found the AGB carbon store of relatively undisturbed peat swamp forests to be within a range of 132-199 t Cha see table below. This ecosystem holds diverse prokaryotic. The results show that the value of LL FC.
The present paper describes the physical and engineering properties of tropical peat soils from Sarawak Malaysia. 2008 most of which was originally covered by forest. However studies on R H are still limited compared with R S in tropical peatland Hirano and others 2014.
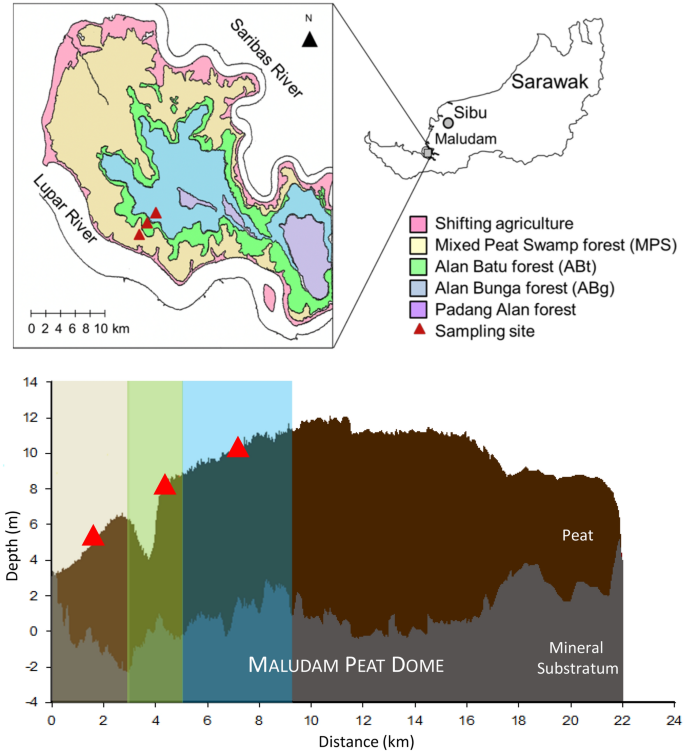
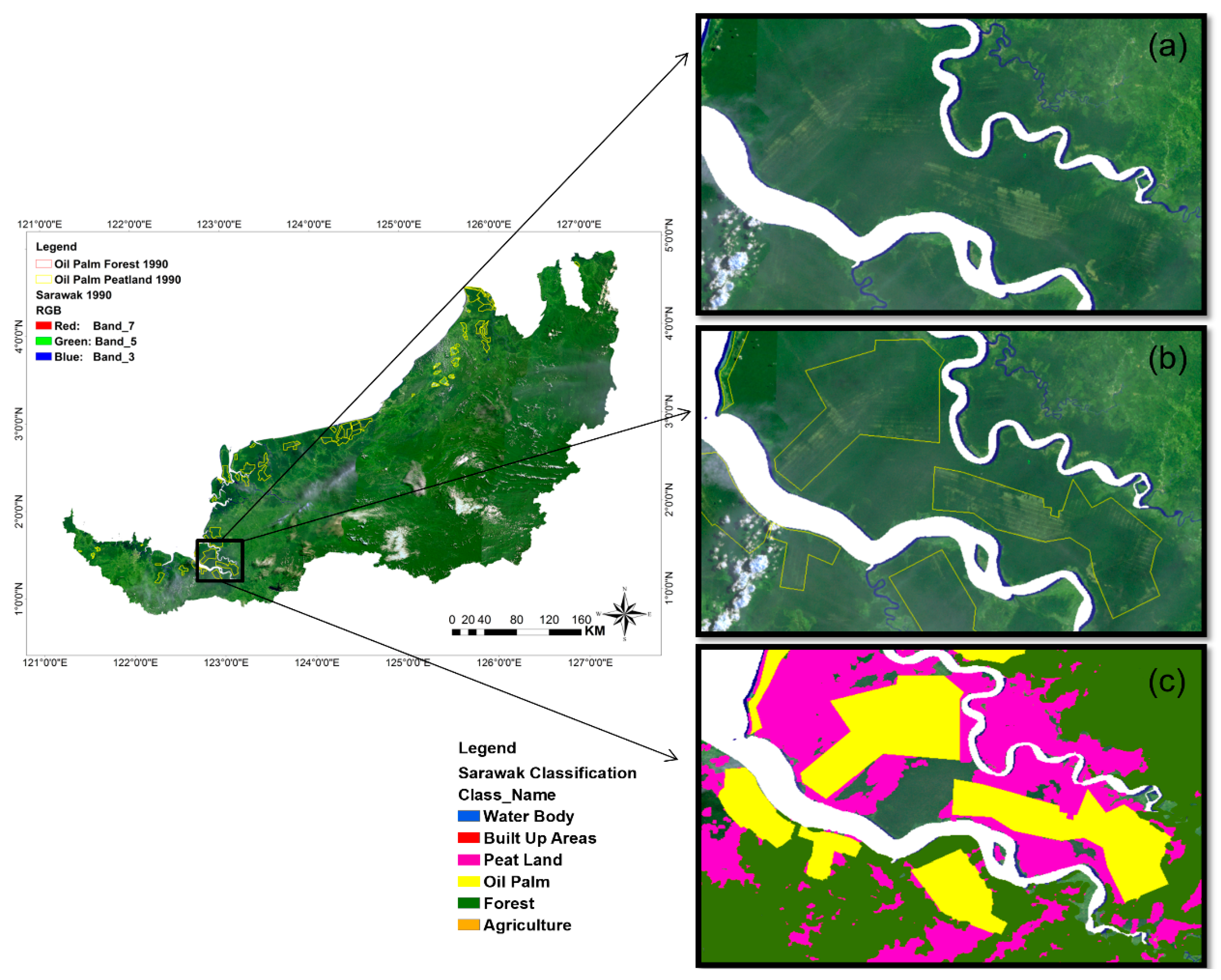
Sarawak has 166 mil ha of peat land with 683 600 ha gazetted as permanent forest Ipor 2006. The study ecosystem is a tropical peat swamp forest in Maludam National Park in the Betong Division of Sarawak Malaysia. In geotechnical field peat soil is defined as soil which is formed by accumulation of purely one hundred percent organic matter and which the distinction between soil and vegetative accumulation is not clear.
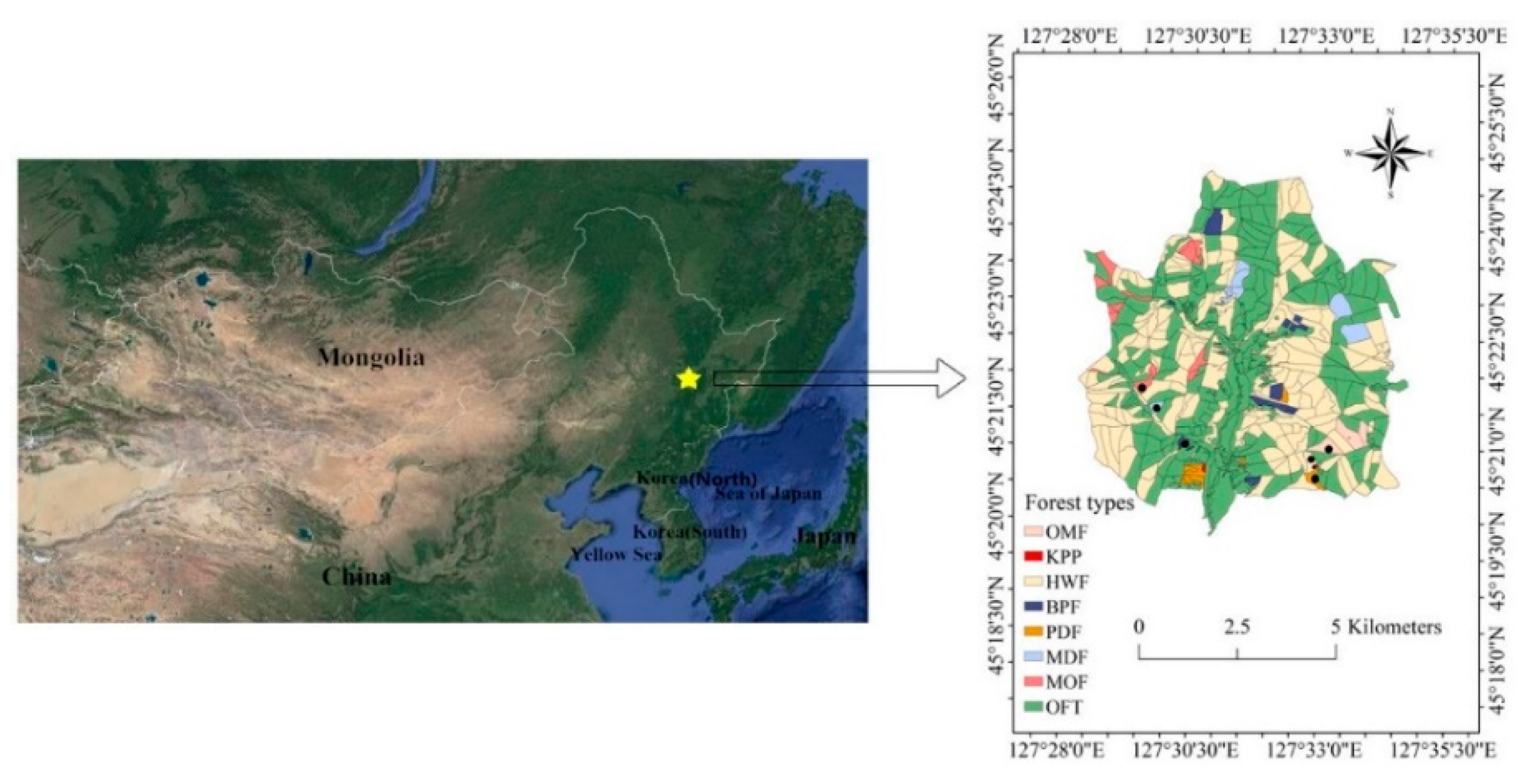
Tropical peat swamp forest is a global store of carbon in a water-saturated anoxic and acidic environment. Anderson 1972 with an average canopy height of 35 m. Tropical peat swamp forests in Sarawak are.
Comparative study between greenhouse gas fluxes from forest and an oil palm plantation on tropical peatland of Sarawak Malaysia. Jauhi-ainen and others 2014. Tropical peat swamp forest is a unique ecosystem in which both swamp forest and peat soil have coexisted over millennia and accumulated a significant amount of soil carbon as peat.
Coexistence of tropical rainforest and waterlogged woody peat is the key characteristic that distinguishes the tropical peat ecosystem from temperate and boreal peatlands. The present paper describes the physical and engineering properties of tropical peat soils from Sarawak Malaysia.